FPC (Flexible Printed Circuit) design involves multiple key aspects, including material selection, layout design, and reinforcement design. Here are some main points of FPC design:
Side keys and main keys usually use 18/12.5 double-sided electrolytic copper to ensure no abnormalities after more than 8 bends.
Connection lines also use 18/12.5 double-sided electrolytic copper to meet connection requirements.
For slider board materials, double-layer slider boards use 1/30Z single-sided glue-free electrolytic copper, while double-sided slider boards use 1/30Z double-sided glue-free electrolytic copper to ensure flexibility and extensibility.
Multi-layer boards use 1/30Z glue-free electrolytic copper to ensure flexibility and extendibility.
Auxiliary materials such as adhesive tape are chosen based on whether SMT (Surface Mount Technology) is required to determine if high-temperature resistant adhesive tape is needed.
FPC design needs to preset basic routes and styles, considering the machine's size and the location of key components.
During circuit design, pay attention to parts where bending and returning applications are used; in principle, use single-sided FPC, while complex circuits use double-sided FPC, and avoid forming holes that affect bending resistance.
FPC design is generally identical to PCB design, but FPC is softer and not convenient for assembly and welding. Thus, rigid materials need to be added to the back of components or non-bending areas like connectors to provide support or facilitate assembly. These rigid materials are called reinforcements.
Reinforcement materials include PI reinforcement, steel plate reinforcement, and FR4 reinforcement. PI reinforcement is suitable for connector boards with plug-in fingers, steel plate reinforcement should be careful to avoid short circuit risks, and FR4 reinforcement is used in other positions that need increased thickness and rigidity.
FPC design also needs to consider current capacity, thermal preset, copper foil thickness used in conductor parts, etc., to ensure circuit insulation and durability.
Hard and soft combination boards combine the lightness and free bending properties of flexible circuit boards with the stability and high efficiency of rigid circuit boards, suitable for products with high demands on performance and reliability such as wearable technology and smart devices.
The above points can effectively guide FPC design to meet the needs of different electronic products.
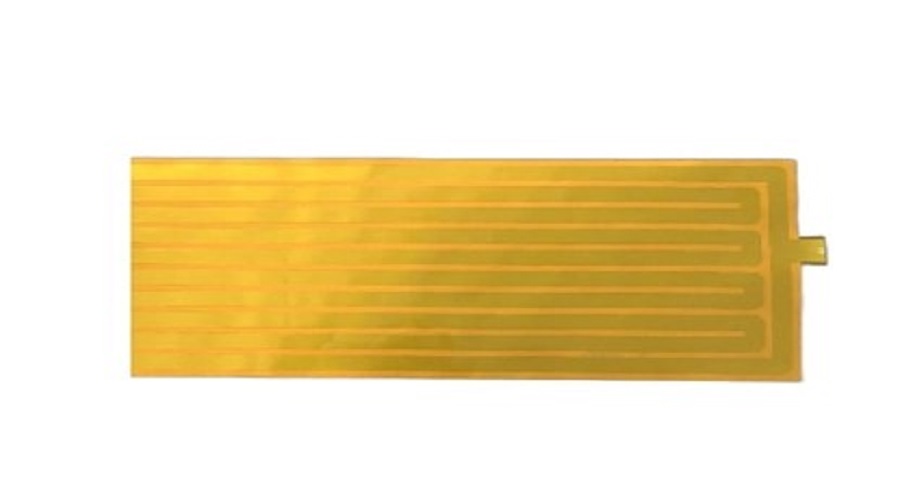 Advantages and Applications of Polyimide Film Heater
16 Apr 2025
Polyimide film heater is a high-performance electric heating element made by using polyimide film as the outer insulation layer, metal foil or metal wire as the inner conductive heating element, and b...
Advantages and Applications of Polyimide Film Heater
16 Apr 2025
Polyimide film heater is a high-performance electric heating element made by using polyimide film as the outer insulation layer, metal foil or metal wire as the inner conductive heating element, and b...
 Call us on:
Call us on:  Email Us:
Email Us:  No.198 Houxiang Road, Haicang District, Xiamen, China
No.198 Houxiang Road, Haicang District, Xiamen, China